The Role of Blockchain in Enhancing Digital Identity Protection
Introduction
In an increasingly digitized world, the concept of identity has transcended the physical realm to become a complex web of online identifiers. The rise of digital identity brings numerous benefits but also significant challenges, particularly in terms of security and privacy. Because traditional identity management techniques are frequently centralised, they are susceptible to abuse and security lapses. Enter blockchain technology, which promises to revolutionize digital identity protection through its decentralized, secure, and transparent nature.
Definition
Blockchain identity management uses a distributed trust paradigm to offer a safe, decentralised solution that provides real-time information about a business or an individual. It enables tamper-proof distribution of encryption keys and asymmetric identity holder verification through decentralised public key infrastructure (DPKI). By reducing the amount of time and manual labour needed to provide identities, it streamlines procedures for clients.
Understanding Digital Identity
Digital identity refers to the collection of information used by computer systems to represent a person, organization, or device. It includes various attributes such as usernames, passwords, social security numbers, and biometric data. The management of these identities is crucial for accessing online services, conducting transactions, and ensuring security in the digital landscape. However, problems like identity theft, data breaches, and a lack of user control over personal information are common with traditional identity management systems.
The Blockchain Advantage
Blockchain technology, originally developed as the underlying infrastructure for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, has far-reaching applications beyond digital currency. Fundamentally, blockchain functions as a decentralised ledger that logs transactions via a computer network. This decentralized nature, combined with cryptographic security, makes blockchain an ideal candidate for enhancing digital identity protection.
1. Decentralization and Reduced Single Points of Failure
Traditional identity systems are usually centralized, meaning they rely on a single authority or database. This centralization creates a single point of failure, which can be exploited by hackers to gain access to a vast amount of sensitive data. Blockchain, on the other hand, disperses information among nodes in a network. This decentralization makes it significantly harder for attackers to compromise the entire system, thereby enhancing security.
2. Enhanced Security Through Cryptography
Blockchain utilizes advanced cryptographic techniques to secure data. Each transaction on a blockchain is encrypted and linked to the previous transaction, creating a chain of records that is immutable and tamper-proof. This immutability ensures that once a digital identity is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted without consensus from the network. This feature is crucial for maintaining the integrity of digital identities and preventing unauthorized modifications.
3. Improved Privacy and User Control
One of the significant drawbacks of traditional identity systems is the lack of user control over personal data. Once data is shared with an organization, users often have little say in how it is used or stored. Blockchain technology offers a solution through the concept of self-sovereign identity (SSI). With the help of SSI, people are able to take ownership of and manage their digital identities independently of centralised authorities. Users can store their identity data on a blockchain and share it selectively with service providers, ensuring that they retain control over their information and reduce the risk of data misuse.
Practical Applications of Blockchain in Digital Identity Protection
The theoretical advantages of blockchain in enhancing digital identity protection are compelling, but real-world applications demonstrate its practical benefits.
1. Decentralized Identity Platforms
Several projects and platforms are leveraging blockchain to create decentralized identity solutions. Microsoft’s Azure Active Directory and the Sovrin Foundation are examples of initiatives that use blockchain to provide secure and user-centric identity management. These platforms allow users to create, manage, and verify their digital identities without relying on a central authority, thereby reducing the risk of breaches and enhancing privacy.
2. Secure Authentication and Verification
Blockchain can also streamline and secure authentication processes. Traditional authentication methods, such as passwords and security questions, are often vulnerable to phishing attacks and credential theft. Blockchain-based authentication can leverage cryptographic keys and smart contracts to enable secure and passwordless authentication. For instance, uPort, a self-sovereign identity platform, uses blockchain to allow users to authenticate themselves without revealing sensitive information, thus enhancing security.
3. Identity Verification in Financial Services
The financial industry is particularly vulnerable to identity fraud and compliance challenges. Blockchain technology can help financial institutions verify customer identities more securely and efficiently. By using blockchain for Know Your Customer (KYC) processes, banks can reduce the risk of fraud and comply with regulatory requirements without compromising customer privacy. Additionally, blockchain can facilitate secure and seamless cross-border identity verification, which is crucial for global financial transactions.
4. Health Records and Personal Data Protection
The healthcare industry deals with highly sensitive personal data, making it a prime candidate for blockchain-based identity protection. Blockchain can enable patients to own and control their health records, deciding who can access and share their information. This method improves the accuracy and interoperability of health data while simultaneously enhancing privacy. Projects like MedRec and Guardtime are pioneering the use of blockchain in healthcare to protect patient identities and ensure data integrity.
Challenges and Considerations
Blockchain has a lot of potential to improve digital identity protection, but it is not without its difficulties. The technology is still in its nascent stages, and widespread adoption will require overcoming several hurdles.
1. Scalability
Blockchain networks must be scalable to handle the vast amount of data associated with digital identities. Current blockchain infrastructures, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, face scalability issues, leading to slower transaction times and higher costs. Developing scalable solutions that can efficiently manage digital identities on a global scale is crucial for the technology’s success.
2. Interoperability
Identity systems built on blockchains need to work with other blockchains and current identity management systems in order to be successful. Creating standards and protocols for interoperability will be essential to ensure seamless integration and widespread adoption.
3. Regulatory and Legal Considerations
The regulatory landscape for blockchain and digital identity is still evolving. Governments and regulatory bodies must establish clear guidelines and frameworks to address issues such as data privacy, compliance, and legal recognition of blockchain-based identities. Balancing innovation with regulatory compliance will be crucial for the successful implementation of blockchain in digital identity protection.
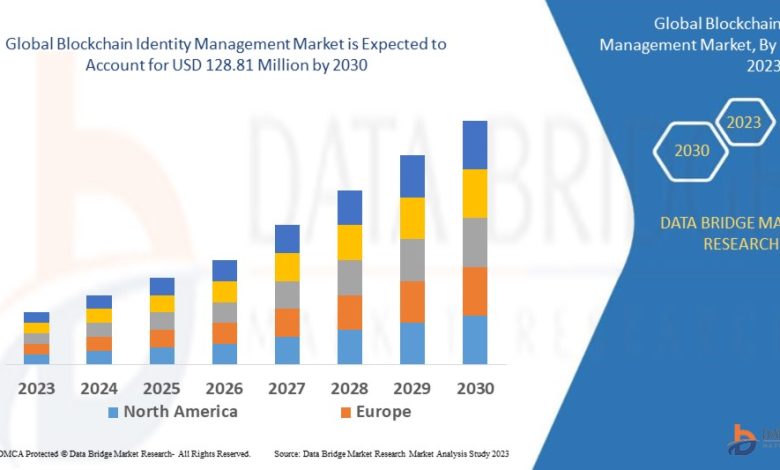
Growth Rate of Blockchain Identity Management Market
According to Data Bridge Market Research blockchain identity management market is anticipated to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 82.00% from USD 1.07 million in 2022 to USD 128.81 million by 2030.
To read more click here.
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-blockchain-identity-management-market
Conclusion
Blockchain technology holds immense promise for revolutionizing digital identity protection. Its decentralized, secure, and user-centric nature addresses many of the vulnerabilities associated with traditional identity management systems. By enhancing security, improving privacy, and giving users control over their identities, blockchain has the potential to transform how we manage and protect digital identities in the digital age. As the technology matures and overcomes existing challenges, it will likely play a pivotal role in creating a more secure and privacy-focused digital landscape.



