When it comes to the fundamental concepts in circuits that electrical and electronics engineers need to know about, there are very few as fundamental in importance as voltage division.
If you wish to analyse and design electronic systems, it will be essential for you to be well-versed in voltage division – including, of course, how to calculate it.
What Is Voltage Division?
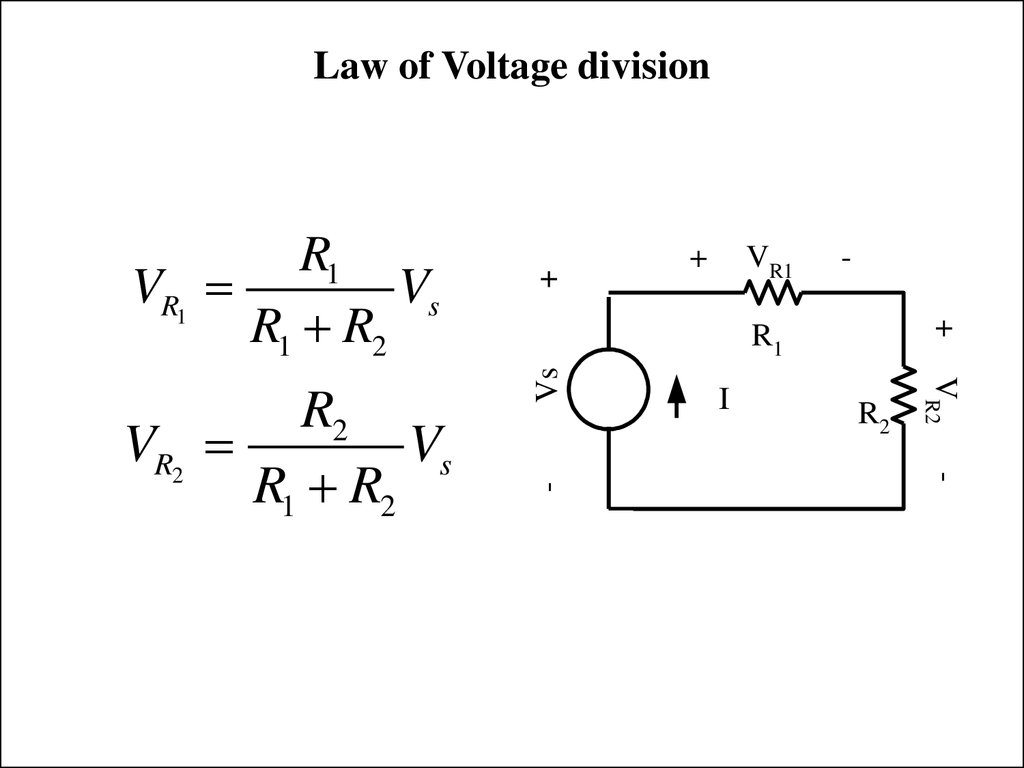
The term “voltage division” refers to the process by which voltage is distributed across components in a series circuit, where the voltage is split proportionally to the resistance of each component.
In the event, then, that you are seeking to create a lower voltage from a higher one using resistors or other components connected in series, this is a way to do it.
A “voltage divider” can therefore be defined as a simple electrical circuit that brings down a larger voltage to a smaller, proportional voltage.
5 Steps to Calculate Voltage Division in Your Next Electrical Project
With no further ado, then, here are the basic steps of calculating voltage division:
-
Understand The Voltage Divider Rule
To grasp voltage division, it is crucial to be familiar with the voltage divider rule, which describes how voltage is distributed across resistors connected in series. It states that the voltage across a specific resistor in a series circuit is proportional to the ratio of its resistance to the circuit’s total resistance.
The formula can be expressed as Vout = Vin * (R2 / (R1 + R2)), where Vout refers to the output voltage (across R2), Vin is the input voltage, R1 is the first resistor, and R2 is the second resistor.
-
Identify The Series Circuit
You will need to check that the resistors in your circuit are connected in series. This means they are arranged end-to-end along a single path for current flow – as a result of which, the same current passes through each resistor in the series.
Once you have determined this, you must make sure you also know the values of the input voltage (Vin), the resistance of each resistor in the circuit (R1, R2, and so on), and the specific resistor across which you want to calculate the voltage.
-
Calculate The Total Resistance
This stage is as simple as adding the individual resistances together, to come up with the total resistance of the resistors connected in series.
So, for example, if you have resistors with resistances of R1 and R2, the calculation of the total resistance can be expressed as RT = R1 + R2.
-
Apply The Voltage Divider Formula
Now, for each resistor, you can calculate the voltage across it by using the aforementioned formula, Vout = Vin * (R2 / (R1 + R2)).
You might have many different resistors in the given circuit. In that case, to figure out the voltage across multiple resistors, you can simply repeat the calculation for each one.
-
Verify The Results
Finally, you should check that the sum of the voltages across all resistors is equal to the input voltage, using the formula Vin = V1 + V2 + … Vn.
Online calculators can also be handy for quickly verifying your manual calculations. The process of how to use a voltage divider calculator for circuits, such as the one on the RS website, is simple: by entering the values for input voltage and each resistor, and clicking ‘Calculate’, you will be immediately presented with the display voltage.
If you know the current (I) in the circuit, you should also check that your calculations are consistent with Ohm’s Law. This will involve the formula V = I * R, where V is the voltage and R is the resistance.
There you have it; the essentials of calculating voltage division in electrical circuits. Don’t forget that only series circuits are subject to the voltage divider rule; in the case of parallel circuits or complex networks, other methods such as Kirchoff’s laws or mesh analysis may be necessary.